Absolute and Partial (Linear Select) Decoding
Absolute and Partial (Linear Select) Decoding
There are two kinds of address decoding techniques. These are
- Absolute Decoding — also known as Full Decoding.
- Linear Decoding — also known as Partial Decoding.
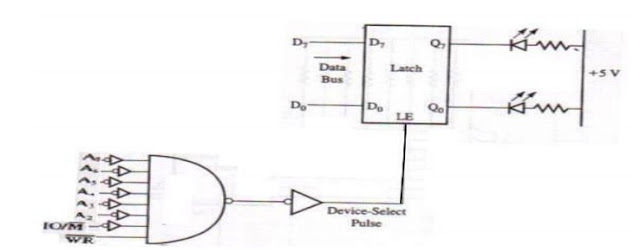
In Figure:- A all eight address line are decoded to generate one unique output pulse; the device will be selected only with the address, 01H. This is called Aboslute Decoding and is a good design practice. However, to minimize the cost, the output port can be selected by decoding some of the address lines, as figure:-B this is called Partial Decoding. as a result, the device has multiple addresses (similar to foldback memory addresses).
Figure A:- Aboslute Decoding
The Partial Decoding is a commonly used technique in small systems. such multiple addresses will not cause any problems, provided these addresses are not assigned to any other output ports.
Figure B:- Partial Decoding
Full Address Decoding (Absolute Decoding) | Partial Address Decoding (Linear Decoding) |
1. All higher address lines are decoded to select the memory or I/O device. 2. More hardware is required to design decoding logic. 3. Higher cost for decoding circuit. 4. No Multiple addresses. 5. Used in large system. 6. Future memory expansion is easier. 7. No bus contention problem. | 1. Few higher address lines are decoded to select the memory or I/O device. 2. Hardware required to design decoding logic is less and sometimes it can be eliminated. 3. Less cost for decoding circuit. 4. It has a advantage of multiple addresses. 5. Used in small system. 6. Future memory expansion is difficult. 7. May suffer from bus contention problem. 8. Suffers from the drawback of multiple addresses (also called shadow addresses). |
REFERENCES
- R. S. Gaonkar, Microprocessor Architecture, Programming, and Applications with the 8085, Fifth Edition, Penram International Publishing (India) Private Limited.
- S Ghoshal, Microprocessor Based System Design, Macmillan India Limited, 1996
- M. Mano, Digital Logic and Computer Design, Prentice – Hall India
- B. Ram - Fundamentals of Microprocessor and Microcontrollers
- “Microprocessors: Principles and Applications” by A Pal
- “Microprocessors and Microcontrollers : Architecture, Programming and Interfacing Using 8085, 8086 and 8051” by Soumitra Kumar Mandal
- “Introduction to Microprocessors and Microcontrollers” by Crisp John Crisp
- “Microprocessors And Microcontrollers” by A Nagoor Kani
- “Microprocessors And Microcontrollers : Architecture, Programming and System Design 8085, 8086, 8051, 8096” by KRISHNA KANT
- “8 - Bit Microprocessor” by Vibhute

Comments
Post a Comment